And the network data transfer speed is determined by the power of the router transmitter to which the signal will be transmitted. The greater the transmitter power, the greater the distance communication can be established. Transmit power is usually measured in milliwatts or dBm. Therefore, if you need to ensure maximum communication range, then use a high-power transmitter and an antenna with high gain.
How can I increase the power of my router?
The unit of power is one Watt and power is denoted by Watts. In radio engineering, it is customary to use another scale, in the so-called “Decibels per milliwatt”, dBm. Zero dBm is 1 milliwatt. Three dBm – 2 mW, etc. In principle, it is enough to remember the reference values: 20 dBm is 100 mW or 0.1 W, and 23 dBm is equal to 0.2 Watt.
Manufacturers of network equipment indicate the transmitter power value in “dBm”, which can be easily converted to Watts if required.
Setting the transmitter power in routers
Before you increase the power of the router “software”. Study the router settings; as a rule, the value set is not the maximum. The recommended sequence of actions is as follows:
- You need to set the maximum power value in the router.
- Then, we must try to “programmatically” increase the power in subscriber devices.
- If these measures are not enough, instead of an external passive antenna, connect a Wi-Fi amplifier with an external antenna (or an active antenna).
- An amplifier or active antenna can be connected to both the router and subscriber devices.
The output power of amplifiers is usually 2 W or 4 W. Using more powerful solutions violates the law. Additionally, we note the following. The use of transmitters with a power of more than 20 dBm or more than 24 dBm for a basic device is contrary to sanitary requirements. And therefore, it is harmful to health.
A weak WiFi signal is a pressing problem for residents of apartments, country houses and office workers. Dead zones in a WiFi network are typical for both large rooms and small apartments, the area of which even a budget access point can theoretically cover.
The range of a WiFi router is a characteristic that manufacturers cannot clearly indicate on the box: the WiFi range is influenced by many factors that depend not only on the technical specifications of the device.
This material presents 10 practical tips that will help eliminate the physical causes of poor coverage and optimize the range of your WiFi router; you can easily do it yourself.
The radiation from the access point in space is not a sphere, but a toroidal field, shaped like a donut. In order for WiFi coverage within one floor to be optimal, radio waves must propagate in a horizontal plane - parallel to the floor. For this purpose, it is possible to tilt the antennas.

The antenna is a donut axis. The angle of signal propagation depends on its inclination.

When the antenna is tilted relative to the horizon, part of the radiation is directed outside the room: dead zones are formed under the “donut” plane.

A vertically mounted antenna radiates in a horizontal plane: maximum coverage is achieved indoors.
On practice: Mounting the antenna vertically is the easiest way to optimize indoor WiFi coverage.
Place the router closer to the center of the room
Another reason for the occurrence of dead zones is the poor location of the access point. The antenna emits radio waves in all directions. In this case, the radiation intensity is maximum near the router and decreases as it approaches the edge of the coverage area. If you install an access point in the center of the house, the signal will be distributed throughout the rooms more efficiently.
A router installed in a corner transmits some of the power outside the house, and distant rooms are at the edge of the coverage area.

Installation in the center of the house allows you to achieve even distribution of the signal in all rooms and minimize dead zones.
In practice: Installing an access point in the “center” of the house is not always feasible due to the complex layout, lack of sockets in the right place, or the need to lay a cable.
Provide direct visibility between the router and clients
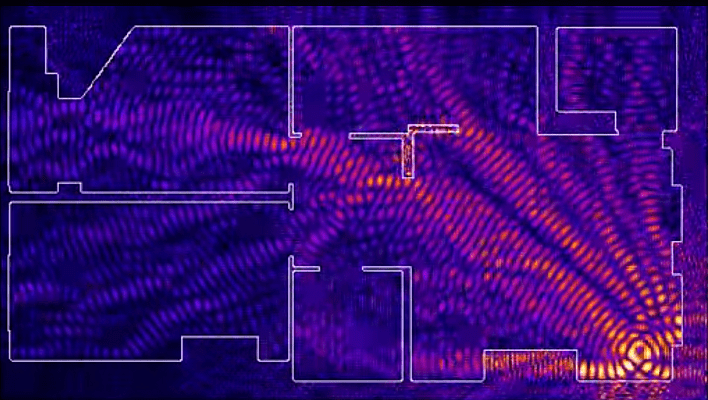
WiFi signal frequency is 2.4 GHz. These are decimeter radio waves that do not bend well around obstacles and have low penetrating ability. Therefore, the range and stability of the signal directly depend on the number and structure of obstacles between the access point and clients.

Passing through a wall or ceiling, an electromagnetic wave loses some of its energy.
The amount of signal attenuation depends on the material the radio waves travel through.
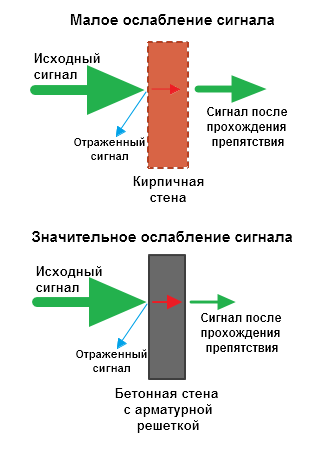

*Effective distance is a value that determines how the radius of a wireless network changes in comparison with open space when a wave passes an obstacle.
Calculation example: WiFi 802.11n signal propagates under line-of-sight conditions over 400 meters. After overcoming the non-permanent wall between the rooms, the signal strength decreases to 400 m * 15% = 60 m. The second wall of the same type will make the signal even weaker: 60 m * 15% = 9 m. The third wall makes signal reception almost impossible: 9 m * 15 % = 1.35 m.
Such calculations will help calculate dead zones that arise due to the absorption of radio waves by walls.
The next problem in the path of radio waves: mirrors and metal structures. Unlike walls, they do not weaken, but reflect the signal, scattering it in arbitrary directions.
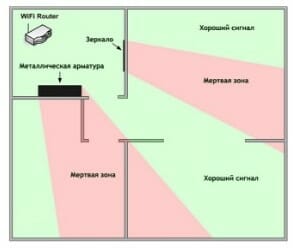
Mirrors and metal structures reflect and scatter the signal, creating dead zones behind them.

If you move interior elements that reflect the signal, you can eliminate dead spots.
In practice: It is extremely rare to achieve ideal conditions when all gadgets are in direct line of sight to the router. Therefore, in a real home, you will have to work separately to eliminate each dead zone:
- find out what interferes with the signal (absorption or reflection);
- think about where to move the router (or piece of furniture).
Place the router away from sources of interference
The 2.4 GHz band does not require licensing and is therefore used for the operation of household radio standards: WiFi and Bluetooth. Despite the low bandwidth, Bluetooth can still interfere with the router.
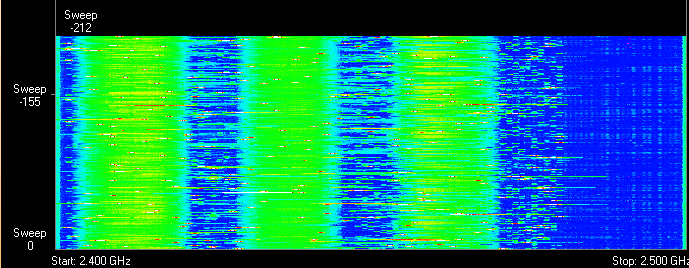
Green areas - stream from the WiFi router. Red dots are Bluetooth data. The proximity of two radio standards in the same range causes interference, reducing the range of the wireless network.
The magnetron of a microwave oven emits in the same frequency range. The radiation intensity of this device is so high that even through the protective screen of the furnace, the magnetron radiation can “illuminate” the radio beam of the WiFi router.

Microwave oven magnetron radiation causes interference on almost all WiFi channels.
On practice :
- When using Bluetooth accessories near the router, enable the AFH parameter in the settings of the latter.
- The microwave is a powerful source of interference, but it is not used very often. Therefore, if it is not possible to move the router, then you simply won’t be able to make a Skype call while preparing breakfast.
Disable support for 802.11 B/G modes
WiFi devices of three specifications operate in the 2.4 GHz band: 802.11 b/g/n. N is the newest standard and provides greater speed and range compared to B and G.

The 802.11n (2.4 GHz) specification provides greater range than legacy B and G standards.
802.11n routers support previous WiFi standards, but the mechanics of backward compatibility are such that when a B/G device appears in the N-router's coverage area - for example, an old phone or a neighbor's router - the entire network is switched to B/G mode. Physically, the modulation algorithm changes, which leads to a drop in the speed and range of the router.
In practice: Switching the router to “pure 802.11n” mode will definitely have a positive effect on the quality of coverage and throughput of the wireless network.
However, B/G devices will not be able to connect via WiFi. If it is a laptop or TV, they can be easily connected to the router via Ethernet.
Select the optimal WiFi channel in the settings
Almost every apartment today has a WiFi router, so the density of networks in the city is very high. Signals from neighboring access points overlap each other, draining energy from the radio path and greatly reducing its efficiency.

Neighboring networks operating at the same frequency create mutual interference, like ripples on the water.
Wireless networks operate within a range on different channels. There are 13 such channels (in Russia) and the router switches between them automatically.
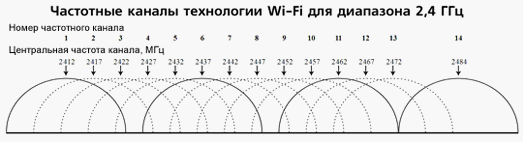
To minimize interference, you need to understand which channels neighboring networks operate on and switch to a less loaded one.
Detailed instructions for setting up the channel are provided.

In practice: Selecting the least loaded channel is an effective way to expand the coverage area, relevant for residents of an apartment building.
But in some cases there are so many networks on the air that not a single channel provides a noticeable increase in WiFi speed and range. Then it makes sense to turn to method No. 2 and place the router away from the walls bordering neighboring apartments. If this does not bring results, then you should think about switching to the 5 GHz band (method No. 10).
Adjust the router transmitter power
The power of the transmitter determines the energy of the radio path and directly affects the range of the access point: the more powerful the beam, the further it hits. But this principle is useless in the case of omnidirectional antennas of household routers: in wireless transmission, two-way data exchange occurs and not only clients must “hear” the router, but also vice versa.
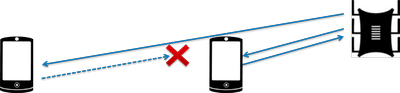
Asymmetry: the router “reaches” a mobile device in a distant room, but does not receive a response from it due to the low power of the smartphone’s WiFi module. The connection is not established.
In practice: The recommended transmitter power value is 75%. It should be increased only in extreme cases: turning the power up to 100% not only does not improve the quality of the signal in distant rooms, but even worsens the stability of reception near the router, since its powerful radio stream “clogs” the weak response signal from the smartphone.
Replace the standard antenna with a more powerful one
Most routers are equipped with standard antennas with a gain of 2 - 3 dBi. The antenna is a passive element of the radio system and is not capable of increasing the flow power. However, increasing the gain allows you to refocus the radio signal by changing the radiation pattern.

The higher the antenna gain, the further the radio signal travels. In this case, the narrower flow becomes similar not to a “donut”, but to a flat disk.

There is a large selection of antennas for routers with a universal SMA connector on the market.



In practice: Using an antenna with high gain is an effective way to expand the coverage area, because simultaneously with the signal amplification, the sensitivity of the antenna increases, which means the router begins to “hear” remote devices. But due to the narrowing of the radio beam from the antenna, dead zones appear near the floor and ceiling.
Use signal repeaters
In rooms with complex layouts and multi-story buildings, it is effective to use repeaters - devices that repeat the signal from the main router.


The simplest solution is to use an old router as a repeater. The disadvantage of this scheme is that the throughput of the child network is half as much, since along with client data, the WDS access point aggregates the upstream flow from the upstream router.
Detailed instructions for setting up a WDS bridge are provided.

Specialized repeaters do not have the problem of reducing bandwidth and are equipped with additional functionality. For example, some Asus repeater models support the roaming function.

In practice: No matter how complex the layout, repeaters will help you deploy a WiFi network. But any repeater is a source of interference interference. When there is free air, repeaters do their job well, but with a high density of neighboring networks, the use of repeater equipment in the 2.4 GHz band is impractical.
Use 5 GHz band
Budget WiFi devices operate on the 2.4 GHz frequency, so the 5 GHz band is relatively free and has little interference.

5 GHz is a promising range. Works with gigabit streams and has increased capacity compared to 2.4 GHz.
In practice: “Moving” to a new frequency is a radical option, requiring the purchase of an expensive dual-band router and imposing restrictions on client devices: only the latest models of gadgets work in the 5 GHz band.
The problem with WiFi signal quality is not always related to the actual range of the access point, and its solution broadly comes down to two scenarios:
- In a country house, most often it is necessary to cover an area in free air conditions that exceeds the effective range of the router.
- For a city apartment, the range of a router is usually sufficient, but the main difficulty is eliminating dead zones and interference.
The methods presented in this material will help you identify the causes of poor reception and optimize your wireless network without resorting to replacing the router or the services of paid specialists.
Found a typo? Select the text and press Ctrl + Enter
A router, also known as a router, is a network device that allows you to choose the optimal direction for transmitting data from the provider to computers, laptops and smartphones of users wirelessly.
The absence of wired communication means the transmission of information through electromagnetic radiation. Since routers operate at ultra-high frequencies, the question is completely legitimate: is the radiation from it harmful? The results of some studies refute these fears, while others confirm them. Let's look at the arguments on both sides.
Why radiation from a wifi router can be dangerous
Descriptive argumentation is not as powerful as the exact technical specifications of the device in question. So let's look at the numbers. The Wifi router operates in the frequency range of 2.4 GHz, and the power of ordinary routers is ~100 μW. When this frequency affects the cells of the human body, the molecules of water, fat and glucose come together and rub together, accompanied by an increase in temperature.
Such frequencies are provided by nature for the exchange of intracellular information between organs and systems of the body. Long-term, external exposure to this range from wireless local networks can cause dysfunction in the process of cell growth and division.
The harm of wifi radiation is aggravated by the radius and speed of data transmission. An excellent illustration of this fact is the enormous speed of transfer of a large amount of information when downloading videos, photographs and other data. The transmitting medium is air, and the carrier frequency is the mid-wave frequency range. And, since our cells are capable of transmitting and receiving energy at different frequencies, the negative impact of the router’s frequency range is quite acceptable.
Residents of apartment buildings may be affected by multiple routers installed in neighboring apartments. Brick walls and metal structures only partially reduce the range of the router, but do not completely delay its radiation. Add to this wireless Internet access points in offices, shopping centers, and cafes. It becomes clear that a person is exposed to radiation from a wifi router almost around the clock.
Moreover, many users do not turn off their wifi router even at night. Summarizing this information, we can conclude that our body is in a constant fight against this aggressive factor. Perhaps this is why even a night's sleep does not bring complete restoration of strength to many, and the immune system does not protect us well from many infections and viruses.
Is a wifi router really that harmful?
 Of course, you have to pay for the convenience of wireless Internet use. But health is too high a price. Is radiation from a Wi-Fi router really dangerous?
Of course, you have to pay for the convenience of wireless Internet use. But health is too high a price. Is radiation from a Wi-Fi router really dangerous?
To assess the effect of this radiation on the human body, a special parameter was introduced, called the absolute optical radiation power. Its unit of measurement is 1 decibel milliwatt (dBm). The average power of a mobile phone is 27 dBm, while the same value for a router is 20 dBm.
Further, the router is never located at such a close distance as a mobile phone. Usually it is 1–2 meters. Do not forget that the radiation power decreases in direct proportion to the increase in the square of the distance to the “culprit” of the radiation.
If somewhere in the subconscious there is still a simmering anxiety about this radiation, you can try to reduce the radiation from the router. Each of the devices for this purpose provides signal power adjustment. Few people pay attention to this function, and almost all users' routers, while maintaining the factory settings, are turned on at full power. By setting the transmitter power to 50, 25% or even 10%, you can significantly reduce the radiation dose and coverage area.
 And by following this operation with your neighbors, you can reduce the level of radiation by tens and hundreds of times. Moreover, manufacturers often unreasonably inflate the power of these devices to increase sales.
And by following this operation with your neighbors, you can reduce the level of radiation by tens and hundreds of times. Moreover, manufacturers often unreasonably inflate the power of these devices to increase sales.
Is it possible to protect yourself from router radiation? Of course, router radiation has an impact on humans. But there is no clear answer yet as to how harmful Wi-Fi radiation is.
But there are these numbers:
- the signal intensity of a Wi-Fi router is 100,000 times weaker than that of a microwave oven;
- The radiation from two routers and twenty laptops is equivalent to the radiation from one mobile phone.
If these impressive comparisons do not reassure the most inveterate skeptic, the following simple rules will tell you how to protect yourself from wifi radiation:
- install routers at a distance of at least 40 cm from your workplace, and certainly not sleep next to a switched-on router;
- turn off your access point if you do not intend to use the Internet;
- Do not keep the laptop on your lap.
Technologies for protection against electromagnetic smog

The background created by electromagnetic radiation is called electromagnetic smog. Naturally, attempts are being made to protect ourselves from all these pathological influences at once.
- Enterprising manufacturers have launched the production of wallpaper that can shield Wi-Fi radiation emanating from neighboring apartments. You can purchase them through foreign online stores. However, this particular product will interfere with internet transmission to other rooms within the apartment.
- A new product has appeared on the health market - a corrector of the functional state of the body (FSC). Among the wide range of products for this purpose, a fabric blanket with carbon thread is offered. The material for creating such bedspreads is a special bipolar fabric that can reflect electromagnetic radiation from computers, wifi routers, phones and other household appliances.
Let's summarize - the above information is based on 4 parameters that allow us to give an objective assessment of whether a Wi-Fi router is harmful to health:
- frequency;
- power;
- distance;
- time.
Each of them works in favor of the theory of its negative influence.
And, although today there are no real facts that can confirm what exactly caused this or that disease, compliance with safety measures will not be superfluous. In addition, humanity does not yet have data on the impact of microwave radiation on future generations.
As it became known, a wireless Internet router uses the same radio frequency as a microwave oven. Thus, one can doubt the safety of this device, without which the modern life of people, equipped with information technology, gadgets and other things, is impossible.
Basic information
A router or router used at home or in an apartment is a special network device that allows you to use the appropriate path regarding data transfer from a specific provider to a PC, smartphone, tablet or laptop.
Wi fi provides a wireless way to send information due to certain electromagnetic emissions. So, how harmful is Wi-Fi to human health, especially for young children? Considering the fact that a wi-fi router operates at a very high frequency, a certain amount of harm to human health is guaranteed. Similar conclusions can be drawn from some studies that confirm or refute this information. It is for this reason that you need to understand what harm a Wi-Fi router does to the human body.
Internet Router Radiation Danger

To determine what harm a wi-fi router causes, it is advisable to refer to the technical characteristics of this equipment. The Wi-Fi router can operate in a certain frequency range, namely 2.4 GHz. As for the power of a standard home router, it is 100 µW. During the influence of this frequency on the human body, friction of molecules and glucose, as well as fat, is observed, which is accompanied by increased temperature.
This frequency was created by nature in order to exchange certain information between the systems and organs of the human body. This is why a Wi-Fi router is harmful to human health, since prolonged exposure to the local network contributes to dysfunction in cell growth and division.
The harmful effects of a wi-fi router are enhanced by the speed, as well as the radius of transmission of specific data. An excellent illustration of this fact is the enormous speed of transmission of massive information that occurs during the downloading of photographs, music, films, and various data. In this situation, air acts as the transmission medium. The harm of a Wi-Fi router can be significant, since the cells of the human body are capable of receiving and transmitting energy at different frequencies.
If a person lives in an apartment, then he can be affected by many routers that are installed throughout the apartment building. Metal structures and brick walls are just a small barrier that reduces the radius of influence of a wi-fi router, but it is unable to completely contain the entire portion of radiation that is harmful to health. Do not forget that all offices, cafes and restaurants, clubs, institutions have wireless Internet access. That is why we can safely say that Wi-Fi radiation is harmful to the health of adults and children around the clock.
Mostly, users do not turn off the wi-fi router even at night, so the body is constantly experiencing the negative influence of aggressive environmental factors. If we summarize this information, we can conclude that a night's sleep cannot bring complete restoration of strength, the immune system weakens, so people often get sick. This is why Wi-Fi is especially harmful for young children.
How harmful is Wi-Fi?

Of course, you have to pay for wireless wi-fi in your own home. However, the health of young children and adults is too high a price! Is Wi-Fi really that bad for your health or is it just another myth?
To correctly assess the amount of harm from a wi-fi router installed at home, you can use special parameters, namely the optical radiation powers. The unit of measurement for this parameter is 1 dBm. As for the power of phones, it is at least 27 dBm, the value of a Wi-Fi router is 20 dBm.
In addition, wi-fi cannot be located as close to a person as a mobile phone. Most often, the distance is about one or two meters, which does not cause such severe harm to human health as from phones. As for the power of Wi-Fi radiation, it noticeably decreases in accordance with the proportional increase in the square of the distance to the Wi-Fi router. In simple words, is wifi as harmful to health as a mobile phone?
Ways to reduce negative impacts

If you are worried about Wi-Fi radiation, then there is an opportunity to reduce the radiation from the wireless router itself. Each Wi-Fi device has a certain level of power, but almost no attention is paid to this. Most Internet users do not interfere with the factory settings of the wi-fi device, leaving the highest power. If you set a different power on the sensor, namely ten, twenty-five percent or fifty, then the wifi router will not be so harmful.
Interesting information regarding wi fi devices:
- 2 wi fi routers and 20 laptops have the same impact as one mobile phone;
- The signal intensity of such a device is one hundred thousand times weaker than that of a microwave oven.
Ways to protect against such radiation:
- if you do not use the Internet, you can turn off the access point;
- fix the devices from the workplace at a distance of forty centimeters;
- Don't sleep with your router turned on.
By following simple rules and recommendations, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from the negative effects of modern technologies that make human life much easier and more convenient. It is advisable to limit a small child from such influence at home, following these recommendations.
Whether Wi-Fi is harmful to human health is of interest to many. Indeed, in the modern world, people cannot imagine their existence without the Internet.
In order to be able to use the World Wide Web anywhere, a wireless method of data transmission called Wi-Fi was invented.
Now you can connect to the Internet wherever it is more convenient. But is it really that useful?
About the Wi-Fi router
In order to distribute a communication signal, a special network device was created. It is called a router or router.
Wireless data transfer and computer connection occurs using radio waves. The principle of operation is similar to the operation of cell phones and radio stations.
The difference is that the Wi-Fi router operates at a higher frequency, which allows you to transmit and receive a large amount of information.
To use wireless communication, you need a router that has a built-in signal reception and transmission module. The same device must be present in the computer.
The router is connected to the Internet via a wire. When receiving information, the device converts it into radio waves, which it transmits to the receiving device (computer or laptop). The PC module receives the signal and makes it digital. The same thing happens in reverse. It is worth noting that the router can distribute a signal to several devices.
However, when the signal is generated, a certain magnetic field is formed, which means that there is a certain radiation on a person. Therefore, sooner or later, any person has a question about whether Wi-Fi is harmful?

Why wifi radiation is harmful to health
Any radiation in large quantities is harmful to human health. As for Wi-Fi, the opinions of many scientists are divided. Some argue that constant exposure to such a signal disrupts the functionality of the body. And others say that it is quite weak, so there is very little harm from it. And who is right in this dispute, and what harm does wi-fi actually cause?
The operating frequency of the router is 2.4 GHz. During its effect on the human body, molecules of water, fat and glucose begin to interact more closely, which leads to an increase in temperature. If such exposure lasts for a long time, then irreversible processes are triggered in the body.
In addition, it is worth noting that electromagnetic radiation is stronger, the larger the area of its influence and the speed of information transmission. This, for example, happens when downloading a “heavy” file. In this case, the harm from the spread of the electromagnetic field is much greater.
Urban residents are affected by Wi-Fi waves almost constantly. After all, routers are currently installed in almost every home, in various establishments, and shopping centers. Many users do not turn off the device even at night, so the radiation continues around the clock.

Based on the results of some studies, doctors concluded that the wireless signal has an effect on some body systems.
Organ systems:
- Brain vessels. After conducting the study, it was found that with prolonged exposure to such a signal, vasospasm occurs, problems with memory and concentration appear. However, it should be noted that the experiment was conducted with school-age children, and their skull bones are thinner than those of an adult.
- Many doctors talk about the dangers of Wi-Fi for a child. However, there are no scientifically proven facts. But parents should pay attention to their child if he spends a long time near the computer, replacing live communication with him. In this case, we can talk more about the dangers of radiation not so much from the router as from the PC.
- Another study was conducted using male sperm. It was noted that in a test tube that stood near the computer for some time while downloading files, twenty-five percent of the sperm were dead. However, when we repeated the experiment, when the Internet was connected via a wire, the result was the same. Therefore, it is wrong to say that wi-fi is to blame. Rather, the culprit is general electromagnetic radiation.
As you can see, there is no exact data that Wi-Fi harms the body. However, it should be remembered that the radiation, although small, is still there. Therefore, certain precautions must be taken.
How to reduce radiation from a wifi router
 What can be done to ensure that wireless Internet rays are safe for health? To do this, you must adhere to certain rules.
What can be done to ensure that wireless Internet rays are safe for health? To do this, you must adhere to certain rules.
Rules:
- For home use, it is better to use wired Internet.
- The Wi-Fi router must be located at least forty centimeters from the workplace. By the way, if the device is located with neighbors, then the radiation from it is minimal.
- When working, do not place the laptop on your lap, and turn off the wireless Internet function on your phone if it is not in use.
- At home, the router should be turned off at night and at times when the Internet is not in use.
- It is better to install the router in a non-residential area, this way you can reduce the harm from radiation.
The most important thing is not to panic. After all, “smart guys” make great money from this by creating foil wallpaper and bedspreads with carbon threads that minimize the harm of wi-fi. If you use wireless Internet correctly, this will not happen.
Wi-Fi is harmful: is it dangerous?
 Currently, a person is surrounded by radio waves from all sides. At the same time, people don’t even think about it. The apartments have a TV, or even more than one, a computer and a microwave oven.
Currently, a person is surrounded by radio waves from all sides. At the same time, people don’t even think about it. The apartments have a TV, or even more than one, a computer and a microwave oven.
And that's the minimum. But there are also radios and cell phones. But no one refuses these devices.
You should know that the power of a Wi-Fi router is 63 mlWatt, and that of a cell phone is one Watt.
In addition, a mobile phone is located much closer to the human body than a router.
Wi-Fi radiation, of course, causes some harm, despite the lack of precise evidence. However, you just need to be careful. This is especially true for parents of small children; you should not allow them to stay indoors with a router for a long time. Yes, and an adult needs to monitor the time of use of such devices.
Video: how harm is caused by WiFi
Wireless Internet routers or Wi-Fi modems use the same radio frequency as microwave ovens. Does this mean Wi-Fi is dangerous to your health?
There is a huge amount of information on this matter on the Internet. There are various reasons for this, the main one being that demand creates supply. And the demand, in turn, arises due to the deterioration of people’s well-being, for which they are trying in every possible way to find an explanation. The harm of Wi-Fi in some articles is confirmed by references to a bunch of studies, while in others it is argued and refuted with evidence.
Of course, Wi-Fi clearly has some effect on health, because even radiation from a monitor affects us. But the question is how significant is this effect on the body, and is it worth paying attention to it at all? Therefore, it is necessary to consider this issue from two sides, and not immediately put forward a separate self-confident opinion.
Arguments that Wi-Fi is unlikely to be harmful to health
- Wi-Fi signal strength is approximately 100,000 times less than that of a microwave oven.
- The intensity of a radio wave, according to the inverse square law, like light, sound and the force of gravity, decreases by a factor of four when moving away from the source by two times. In other words, the signal level drops very quickly. Under normal conditions, Wi-Fi intensity is so low that it's not worth worrying about - it's just part of the "" that radio and television signals, electrical cables, electric motors in household appliances, and the universe as a whole also generate.
- Often, the wavelength of Wi-Fi signals (12 cm) is approximately the same as the cosmic background radiation (0.001 - 0.5 m) that affects us when we go outside. And this cosmic radiation influenced our ancestors in stone caves, so we are partially prepared for it.
- The electromagnetic spectrum includes waves from very long waves—radio frequencies—to very short waves—gamma radiation. At the same time, the light visible to us is somewhere in the middle. We know that types of ionizing radiation with wavelengths shorter than light are generally dangerous. Examples include ultraviolet (UV) rays, x-rays, and gamma rays. The ultraviolet part of sunlight is, of course, also dangerous, which is why sunscreens were invented.
Non-ionizing wavelengths, which are higher in frequency than light, are generally not dangerous. These include infrared rays and radio waves. With a frequency of 2.45 GHz, Wi-Fi travels in the microwave range, in which baby monitors and mobile phones also operate.
Of course, it is possible to do dangerous things with radiation. The sun's rays, with the help of curved mirrors, can set objects on fire; waves in a microwave oven, thanks to a magnetron and high power, boil water. You can even use a high-pressure stream of water to pierce steel, but this does not mean that a person will die from taking a bath or standing under a fountain.
- The mobile phone is near the brain during a conversation, while the Wi-Fi router may well be in another room. And according to some estimates, a person receives a larger dose of microwaves from one 20-minute phone call than from a year of exposure to Wi-Fi, the source of which is not directly near him.
- Twenty laptops and two routers are roughly equivalent to one mobile phone under standard usage conditions.
- The World Health Organization, which has studied this topic in depth, says: “In the field of biological effects and medical applications of non-ionizing radiation, approximately 25,000 papers have been published over the past 30 years. Despite some opinions that there is still some research to be done, scientific knowledge in this area is currently more extensive than for most chemicals. Based on a recent in-depth review of the scientific literature, WHO concluded that evidence does not currently support the existence of any health effects from exposure to low-level electromagnetic fields. However, some gaps in knowledge about the biological effects exist and require further research."
Arguments that Wi-Fi may pose a potential health risk
- In the summer of 2011, the World Health Organization designated electromagnetic fields that come from Wi-Fi, cell phone networks, radio signals, microwave ovens, and cordless home phones as "possibly carcinogenic" agents, along with other things (such as coffee) for which there is evidence harms are not yet clearly confirmed.
- There was a case where a woman doctor noticed that her family members were experiencing sleep disturbances, heart palpitations, migraines, and general poor health, and it all started in the same week. These painful sensations continued further. After eliminating all other possible causes, she turned off the router and they felt better. Fortunately, they did not live in an area inundated with electromagnetic fields from wireless technology from nearby houses. Now, of course, the family uses a wired Internet connection, and the health problems have not returned.
- There are results from a number of studies (2009-2014) on the effects of microwaves with a frequency of 2.4 or 5 GHz (Wi-Fi) on animals and people, which confirm the negative impact on many body functions. According to their results:
- observed the detrimental effects of radiofrequency waves emitted from conventional Wi-Fi devices on the testes of growing rats;
- when using laptop computers connected to the Internet via Wi-Fi, the motility of human sperm decreases and the fragmentation of sperm DNA increases;
- wireless network modulation (2.45 GHz) caused toxic oxidation of melatonin in the mucous membrane of rats;
- as well as a huge number of other results, including effects on the autonomic nervous system, heart rate, brain and spinal cord, effects on the kidneys during pregnancy in rats, etc. All this can be seen in more detail.
- It is impossible in most cases to be far from the source of Wi-Fi waves while using it. After all, even if the router is in a distant room, the device with which you use the Internet (laptop, tablet, smartphone) itself acts not only as a receiver, but also as a transmitter of electromagnetic waves. Therefore, for example, even a smartphone in your pants pocket with Wi-Fi always on creates an electromagnetic field near your genitals. And they are expected to be one of the first to be affected by Wi-Fi.
- Wi-Fi can have the strongest impact on the body in children. For example, a radio-controlled toy can cause no less harm, but its period of operation is insignificant compared to a Wi-Fi source operating in the house. It is believed that these adverse effects of wireless Internet may take many years to appear.
- They started installing Wi-Fi in schools in Israel, several years have passed since then. In 2011, a commission in Europe issued recommendations to ban Wi-Fi and WLAN in schools, as, in their opinion, it could harm the health of students. Some countries did just that. There are lawsuits going on in Israel in which parents are demanding this be done. And France has generally introduced a ban on any type of wireless connections in schools, incl. and mobile communications.
- There are results of studies conducted on plants, for example, on watercress by schoolgirls from Denmark. The seeds affected by Wi-Fi did not germinate. By the way, Denmark generally holds the record for such evidence of the harm of electrosmog.
- It is no longer schoolchildren, but scientists from the same Denmark who, through experiments, have proven the negative impact of Wi-Fi on the human brain and indoor plants. Although this is a dubious source. During their experiments, schoolchildren had to put a smartphone with Wi-Fi turned on under their pillow at night, after which the next day they experienced vascular spasms and poor concentration. But this sounds very subjective and not very convincing. In the second case, they noticed a clear disappearance of indoor flowers in the room where the wireless Internet router was located.
Conclusion
The direct official harm of Wi-Fi, as well as any other similar sources of radio waves (mobile network, radio-controlled devices, Bluetooth headsets, home radiotelephones, etc.) on humans has not yet been proven. Although a lot of research has been carried out on this matter, as a result of which, it seems, Wi-Fi was harmful, but also often its absence.
The main problem is the arbitrarily subjective results, in which, in the case of various negative consequences, the specific process of their manifestation was not justified. But also, everyone understands that usually there is no smoke without fire. Many people claim that they have experienced general malaise, which is possibly caused by the electromagnetic field emanating from a wireless Internet source. Although there were many more cases when health problems manifested themselves in those living near antennas providing mobile communications.
You should be especially careful with children, whose health is most likely to be affected by Wi-Fi. After all, children are more susceptible to radiation than adults. Also, some tips may help to minimize the possible harm from this modern technology.
 Recommendations for reducing possible harm from Wi-Fi
Recommendations for reducing possible harm from Wi-Fi
- Use a Wi-Fi antenna located further away as a signal receiver and transmitter, rather than the device itself. This is primarily suitable for users of desktop PCs that are not initially equipped with a Wi-Fi module. But it is unlikely that laptop owners will connect such an antenna if almost all of these gadgets are equipped with an internal module for such a thing. But for tablet PCs and smartphones this method is not rational at all.
- Try to use cable Internet as much as possible without Wi-Fi. But tablets and smartphones are also left behind.
- If the Wi-Fi source is not yours, then in most cases it is either with your neighbors, or simply in another room, and the damage to Wi-Fi is minimal until you use it. For even more effective protection from its field, you can use foil or other reflective material. This is the principle that a Faraday cage operates on. For the experiment, you can wrap your mobile phone in foil and if you can’t call it, then the experiment was successful. But there are also building insulating materials that contain aluminum to retain moisture and heat. They can also help achieve the Faraday cage effect.
- Turn off the Wi-Fi source in your home when not in use, rather than leaving it on overnight, as most people do. Also disable the function responsible for its operation in your phones, especially when carried in your pocket. And it is highly undesirable to place your mobile phone under your pillow or very close to you while sleeping, because even with wireless Internet reception turned off, this has an adverse effect.
Of course, few people will be willing to sacrifice their comfort in order to protect themselves from possible harm from Wi-Fi. But measures to protect children from this are worth taking. You should especially not allow a small child to stay in the room where the Wi-Fi router is located all day.
In any case, there are more serious health threats than Wi-Fi that we can control. Poor quality food, bad habits, and a passive lifestyle can have a much more negative impact.
Finally, you can watch a video where you can see the presence of radio emissions near the router.
Of course, no one is usually closer than 30 cm to this device, but many people carry a phone with Wi-Fi turned on in their pocket or even sleep next to it.
And is Wi-Fi harmful at all?
Doctors have been arguing about this for many years. And only schoolgirls from Denmark were able to clearly and quickly prove the harm of radiation.
They tested the effect of Wi-Fi on plant seeds. To do this, they first took containers with earth. And ordinary watercress was sown in two of them. After 12 days, sprouts appeared in one of the bowls, which was out of Wi-Fi access. In the other one, which fell into the zone, they never sprouted.
The girls' work is approved by experts. They intend to continue their research in order to prove or, on the contrary, refute the conclusions made.
Wireless Internet is not as safe for health as it seems
We all know about the dangers of mobile phones, laptops, and microwave ovens in terms of radiation. But they forgot about wireless Internet. It turns out that this type of Internet also causes harm that affects our health.
It is very convenient to use WiFi wireless Internet in cafes, shopping centers, and even soon this function will be available in the subway. But few people know that it is wired (a modem with wires).
Of course, the harm from wireless Internet has not been completely proven, but it is known and proven that being in an apartment or room with a WiFi router has an impact on a person’s health. This may not appear immediately, but over time it can make itself felt in the form of headaches, increased blood pressure for no reason, and in some cases, increased heart rate.
Wireless Internet also affects memory; it can deteriorate over time. Radiation from WiFi routers can lead to the development of various tumors, gene changes (DNA damage) and of course, this type of Internet can contribute to premature aging.
A router, also known as a router, is a network device that allows you to choose the optimal direction for data transfer from the provider to computers, laptops and smartphones of users wirelessly....
The BUSINESS TELECOM company presents the top 10 best Wi-Fi routers of 2019. We use all routers in our work, which means we have experienced their pros and cons from our own experience.
Choosing a good WiFi router is not easy. The main criteria for forming the TOP 10 were the stability of the devices, the provided Internet speed and coverage area.
10. D-Link DIR-825/AC
In 10th place in our ranking is the D-Link DIR-825/AC Wi-Fi router - a rational solution for organizing high-speed wireless in a small office, cafe or retail outlet. The router provides a stable connection from any computer or mobile gadget.

The router functions as a base station for organizing access to the Internet network from devices operating according to the 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n and 802.11ac standards.
✔ Benefits:
- Speed up to 300 Mbit/s at 2.4 GHz, up to 867 Mbit/s at 5 GHz.
- Wireless connection speed - up to 1167 Mbit/s.
- Multifunctional USB port.
- Supports WEP and WPA/WPA2 security standards.
- Screens connection requests by MAC address.
- Provides access to WPS and WMM technologies.
✘ Disadvantages:
- Fixed antennas
- Not suitable for large offices and companies, because... has a small coverage area.
- Gets very hot
- Not a particularly user-friendly web interface.
The router of this model is popular among users due to its extensive functionality. This device will protect your network from hacker attacks and block access to unwanted sites for local network users.
9. Asus RT-AC51U
A strong Wi-Fi router that runs on the 802.11ac standard and offers wireless data transfer speeds of up to 733 Mbps. The presence of a USB connector makes it possible to connect printers, external drives and 3G/4G modems, which significantly expand the functionality of the equipment. You can also use it to recharge smartphones, tablets and other gadgets if you don’t have a spare power supply on hand. The developers have created the ASUSWRT interface, which is as convenient and intuitive as possible.

✔ Benefits:
- Speeds up to 300 Mbps in 2.4 GHz mode and up to 433 Mbps in 5 GHz mode.
- Allows you to monitor Internet traffic consumption and limit the speed of the Internet channel for individual applications.
- The coverage area is larger than many models. Asus RT-AC51U is equipped with powerful antennas that increase the wireless network coverage by 150% compared to conventional devices.
- Ability to configure Internet bandwidth usage priority for various applications.
- Possibility of connecting a VPN server.
✘ Disadvantages:
- Wireless data transfer speed is slower than other routers.
- Small coverage area: thick walls can become a significant obstacle.
Built on 5th generation wireless communications technology, users get access to all the latest features. This is one of the best solutions for offices with a small number of employees.
8. TP-Link Archer C60
The TP-Link Archer C60 device continues the rating of Wi-Fi routers, the speed of which reaches 450 Mbit/s at a frequency of 2.4 GHz. This is absolutely enough for sending emails, loading various web pages and working with audio files.

✔ Benefits:
- The 5 GHz channel with speeds up to 867 Mbps provides comfortable viewing of HD video streaming.
- Supports the new 802.11ac standard, which is 3 times faster than 802.11n.
- 5 antennas (three for 2.4 GHz and two for 5 GHz) with alternate installation to optimize simultaneous operation in two bands.
- The network remains as stable as possible and practically immune to various interferences.
- The ability to create a separate guest network for your company's clients.
✘ Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for large offices and companies due to the relatively low data transfer speed.
- Cannot be wall mounted due to antenna placement.
7. Wi-Fi Zyxel Keenetic Ultra II
Seventh place in the list of the best Wi-Fi routers is taken by Zyxel Keenetic Ultra II. The connection to this router is via a dedicated Ethernet line. The provider can use any connection, in particular PPTP, PPPoE, IPv4/IPv6, etc.
Regardless of the selected type and nature of the load, users receive speeds of up to 1000 Mbit/s or up to 1800 Mbit/s for IPoE/PPPoE. The presence of special ports allows you to organize a wireless network using a 3G, 4G, DSL modem, PON terminal with an Ethernet port or a Wi-Fi hotspot (private, from the provider).

✔ Benefits:
- The device is equipped with NDMS 2 OS and a managed switch, so you can combine any connections.
- Dual-band Wi-Fi access point with signal power amplifiers and rotating antennas.
- A convenient interface allows you to configure automatic switching to a backup channel in case of failure of the main network.
- The 2-band network is protected according to the WPA2 standard for all used devices (laptops, PCs, tablets, smartphones, etc.).
- Ability to create a guest network separate from the main network.
- The ability to distribute the load on the channel depending on the application.
✘ Disadvantages:
- The wireless network throughput speed is insufficiently high, which makes the model unsuitable for large offices.
- The model may become very hot.
Keenetic Ultra II is a router with large Wi-Fi coverage that is ideal for medium-sized offices.
6. Asus RT-AC87U
ASUS RT-AC87U is a router with a long Wi-Fi range and high data transfer speeds. In the 5 GHz frequency range it reaches 1734 Mbit/s, and at 2.4 GHz - 600 Mbit/s. In total, the network throughput is 2334 Mbps, which is much faster than using standard 3-channel routers.
The router is equipped with 4 antennas that provide increased signal amplification.

✔ Benefits:
- The device can operate effectively in Multi-user MIMO 4x4 mode.
- Connected computers and gadgets receive maximum connection speed.
- Powered by a powerful 2-core processor and provides high levels of performance.
- An additional processor with 2 cores is used to implement 4x4 Wi-Fi mode, and the overall throughput increases by 50%.
- Two USB ports - standard 2.0 and high-speed 3.0.
- Coverage area - up to 465 m2.
- Excellent price-quality ratio.
✘ Disadvantages:
- Quite large dimensions
- Models can become very hot, so it is recommended to install them in a well-ventilated area.
The user will be able to appreciate the long warranty period and the possibility of use with a wide range of devices. The router is perfect for large rooms and buildings up to 465 m2.
5. D-Link DIR-890L
In fifth place is the powerful D-Link DIR-890L router - a prominent representative of 2-band gigabit routers. It provides high-quality integration of computers and other devices into a single network that provides access to broadband Internet. A special feature of this router is its support for SmartConnect1 technology, thanks to which the wireless connection speed increases to 3200 Mbit/s.
This equipment will be an excellent choice for multi-user operation in two independent wireless networks operating in accordance with the 802.11ac standard. The parameters of each network will be up to 600 Mbit/s at 2.4 GHz and up to 1300 Mbit/s at 5 GHz.

✔ Benefits:
- Wireless connection speed - up to 3200 Mbit/s.
- The developers also took care of expanding the network coverage area by introducing the AC SmartBeam system into the device.
- The router operates stably in two bands at once: 2.4 and 5 GHz.
- Connecting to the Internet channel requires minimal user intervention.
- Smart Connect technology selects the least congested frequency range and connects a new device automatically.
✘ Disadvantages:
- High price. In terms of price-quality ratio, there are more interesting models.
- The dual-core processor runs at just 1 GHz, while most modern routers have a main processor clocked at 1.4 GHz.
DIR-890L is an impeccable wireless network quality, stable Wi-Fi connection and maximum comfort of accessing the Internet through mobile devices.
4. Asus RT-AC88U

✔ Benefits:
- Wi-Fi speed is up to 3167 Mbit/s.
- 4 antennas in the 4T4R configuration (4 transmit and 4 receive) create a large coverage area.
- Asus AiRadar beamforming technology to expand Wi-Fi coverage.
- Dual-core 1.4 GHz processor for high data transfer speeds with devices connected via USB.
- USB 2.0 and 3.0 ports.
- Wired network data transfer speeds up to 2Gbps.
✘ Disadvantages:
- Covers an area of no more than 180 square meters.
- High price.
Ideal for offices and companies that need high-speed Internet that can withstand heavy loads.
3. TP-Link Archer C5400
In third place among the top Wi-Fi routers is the innovative Archer C5400 router with Tri-Band technology. The latter is a real boon for organizing three-channel user networks. This router model boasts a 25% increase in data transfer speed thanks to NitroQAM support.
This is not just a router, but a real network center with great power, which allows you to easily perform various tasks: watch HD video, run online games from several devices at once, etc.

✔ Benefits:
- Speed up to 1000 Mbit/s in 2.4 GHz mode, 2167 Mbit/s in 5 GHz mode.
- High speed ensures the fastest possible response even for the most resource-intensive applications.
- Archer C5400 works with integrated MU-MIMO technology, thanks to which 4 data streams operate simultaneously.
- 8 antennas with Beamforming accurately determine the location of gadgets and send them a powerful Wi-Fi signal.
- The main processor of 1.4 GHz and 3 coprocessors allow you to work in multitasking mode.
- Equipped with USB 2.0 and 3.0 ports.
✘ Disadvantages:
- There are no shortcomings in terms of speed and performance level.
- One of the disadvantages of the model is the rather voluminous body.
This is the optimal router option for offices, cafes, Internet centers, etc., providing connection to a large number of computers and other devices without sacrificing performance.
2. Asus BRT-AC828
Asus BRT-AC828 is rightfully considered one of the best WiFi routers for large offices, IT companies and television companies. This is a powerful router with a long range and can withstand very heavy loads.

✔ Benefits:
- 2 wired Gigabit Ethernet ports with bandwidth up to 2 Gbps.
- Bandwidth of 4 wired ports in the local network is up to 4 Gbit/s.
- High level of network protection equipped with a content filtering system.
- Ability to work with 250 client devices at high speed simultaneously.
- 8 antennas in a 4x4 configuration.
- Wide WiFi coverage area.
✘ Disadvantages:
- High price
The Asus BRT-AC828 model is perfect if you have a large company and many devices that need to be connected to the WiFi network.
1. Asus RT-AC 5300
ASUS RT-AC 5300 was recognized as the best Wi-Fi router according to BUSINESS TELECOM in 2019. Equipped with NitroQAM technology, the router provides unprecedented wireless data transfer speeds - up to 5334 Mbit/s! This is one of the most powerful routers you can find on the market today.

✔ Benefits:
- Adaptive QoS function that allows you to set the priority of using a network connection.
- Capable of serving many client devices without lag. For example, its bandwidth allows you to transmit several video streams in Full-HD format at once.
- 8 antennas provide a large coverage area.
- Data transfer speed in 2.4 GHz mode is up to 1000 Mbit/s, in 5 GHz mode - up to 2167 Mbit/s.
- Technology for distributing network load between 3 channels.
- The 1.4 GHz dual-core processor can withstand high network load.
- USB 2.0 and 3.0 ports
- The ability to combine 2 wired network ports into one with high speeds of up to 2 Gbit/s.
The Asus RT-AC5300 Wi-Fi router has no significant drawbacks. It is ideal for providing a wide and stable WiFi area in buildings, large offices, large television and IT companies. We give it first place in the ranking of the best WiFi routers for business.
Results
You might be interested in services
I decided to prepare an article with tips on strengthening the signal of a Wi-Fi network. On the Internet, there are many different articles on this topic, but in almost every article there is a lot of unnecessary information. More precisely, a lot of recommendations for some settings that have nothing to do with increasing the range of the Wi-Fi signal and cannot in any way affect the range of the network itself.
If we are talking about strengthening the Wi-Fi signal, then of course we will introduce the coverage radius of the network itself, that is, the Wi-Fi range. For example: we bought a router, installed it, configured it, but in the farthest rooms there is no Wi-Fi at all, or the signal level is too weak. Or, the router is installed on the ground floor (where there is a signal), and on the second floor the signal is already very weak or absent altogether. A common situation that many people face, and I’ve encountered this myself.
What determines the range of a Wi-Fi network? There are a lot of different factors: from the router itself (number and strength of antennas), from the walls in your house, from the number of neighboring Wi-Fi networks, from the location of the router, some other interference, etc. Many people ask you to recommend a router that, for example, will provide a stable Wi-Fi signal for a three-room apartment, a private house, and etc. In such cases, it is impossible to advise anything specific. Everyone has different conditions, different walls, etc. The only thing I can advise is to roughly focus on the area of your home. If, for example, you have a one-room apartment, then even an inexpensive router with one antenna with a power of 3 dBi will cope with its task without any problems. Well, if you have a larger house or apartment, then take a more expensive device. Although, price is not always an argument. I have an expensive one, three antennas, some kind of proprietary Asus function that increases the network coverage radius. So, under the same conditions, at the same distance, it does not show much better results than the same one. Which has internal antennas, and is several times cheaper.
How to strengthen the Wi-Fi signal in the router settings?
If you have already purchased and installed a router at home or in the office, and Wi-Fi is not available everywhere you need it, then you can try to strengthen the wireless network. We will now look at how to do this. You can strengthen the signal both using the settings in the router and using separate devices and devices.
1 Search and change the channel on the router. If your devices see many of your neighbors’ networks available for connection, then all these networks can load the channel on which your network operates, and thereby reduce the network’s range.
You can try setting some kind of static channel in the router settings, or setting it to Auto. This is where you need to experiment. If you are not too lazy, then using the inSSIDer program you can find a freer channel and set it in the settings of your router.
I won’t go into detail, I’ll just give you a link to the article. In it, I talked in detail about channels, and how to find an unloaded channel. Also, there are instructions for changing the channel on routers from different manufacturers.
2 We switch our network to 802.11N operating mode. As a rule, by default on all routers the wireless network operates in mixed mode b/g/n (11bgn mixed). If you force the router to broadcast Wi-Fi in 802.11N operating mode, this can increase not only the speed, but also the Wi-Fi coverage range (if your router has more than one antenna).
The only problem is that if you have older devices that don't support 802.11N mode, they simply won't see your network. If you don't have any older devices, then don't hesitate to switch your network to n mode. It's very easy to do. We go into the router settings, usually at the address 192.168.1.1, or 192.168.0.1 (see detailed instructions on entering the settings).
In settings, open the tab where you configure the wireless network. They are usually called like this: Wi-Fi, Wireless mode, Wireless network, Wireless, etc. Find the item there Wireless mode(Mode) and set it to N only. That is, the network operates only in N mode.
For example: changing the wireless network mode on an Asus router

Save the settings and reboot the router. If you have problems connecting devices, return the mixed mode back.
3 We check the transmission power in the router settings. On some routers, it is possible to set the power level of the wireless Wi-Fi network. As far as I know, the default is maximum power. But, you can check.
In Asus routers, these settings can be changed on the tab Wireless network - Professionally. At the very bottom, there is a point " Tx power control". There is a scale that can be adjusted in percentages. It looks like this:

On Tp-Link routers, open the tab Wireless - Wireless Advanced. Paragraph Transmit Power allows you to adjust the signal strength. The High value means maximum power.

These settings will be more useful if you want, on the contrary, to reduce the signal strength of your Wi-Fi router.
How to increase the range of a Wi-Fi network using additional devices?
1 Installing a repeater, or setting up a second router in amplifier mode. Of all the recommendations that you will see here, or generally find on the Internet, this method is the most effective and reliable. True, you will have to spend money on a repeater.
Ordinary routers can act as a repeater. Here are the instructions for setting up ZyXEL and Asus routers in repeater mode:
If your Wi-Fi does not reach some rooms, then installing a repeater will solve this problem. And if you have a house with several floors, then you can install a router on the first floor, and a repeater on the second. Excellent and working scheme.
2 Changing the router antennas to more powerful ones. If your router has removable antennas, you can buy more powerful ones, and thereby slightly increase the coverage of your network. Why a little? Yes, because replacing antennas usually does not give a very good result. It is there, but not enough to increase the radius by several rooms. In any case, you will have to spend money on antennas. And it seems to me that this money would be much better spent on a repeater. Yes, it will cost more, but the benefits from it are much greater.

If you decide to change antennas, then take powerful ones with a gain of 8 dBi. But they are expensive, and several of these antennas will cost as much as a repeater.
I already wrote, you can see the results.
3 Buying a new router, switching to 5 GHz. You can buy a more powerful, expensive router. Better yet, a router that supports the 5 GHz band. What is the advantage of the 5 GHz range? It is practically free, now most all networks and other devices operate in the 2.4 GHz range. Less interference means more speed and more stable network operation.
There are places where a 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi network practically does not work. It glitches all the time, connection drops, low speed, etc. And all because there are so many different networks. In such cases, switching to 5 GHz solves all problems.
But network coverage in the 5 GHz band will be less compared to the 2.4 GHz band. This is a feature of the 5 GHz frequency.
1 Select the correct location for your router. This is actually very good and effective advice. As a rule, everyone installs routers at the entrance, or in some distant rooms. The correct location of the router will allow the signal to be distributed correctly, thereby increasing the Wi-Fi range.
Simply put, you need to install the router as close to the center of the house as possible. Yes, this does not always work out, since you need to lay a cable to the router, and pulling it to the middle of the house is not very convenient. But even minor movements of the router can increase the network level in the rooms you need. Also, you need to remember that walls are the enemy of Wi-Fi networks.
2 Homemade amplifiers for Wi-Fi antennas. You can find many instructions that show how to make amplifiers for a router. As a rule, this is ordinary foil and tin cans. It turns out that if we place a sheet of foil on one side of the antenna, the signal will bounce off it and be directed in the direction we need.

I think this is all nonsense. Firstly, a cut beer can or a piece of foil on the back of the router doesn’t look very nice, and secondly, it has practically no effect. You can check.
These are the tips. I think you have found a suitable way for yourself to increase the range of your Wi-Fi network. Share your tips in the comments!
