The development of regulatory documentation is one of the main stages in the implementation of security systems, on which the further effectiveness of their use in your company directly depends. In this article, we will analyze the basic requirements of legislation and regulators for the use of information security systems in an organization, which should be taken into account during the implementation of DLP.
So, what is a DLP system? A DLP system is a software product designed to prevent leaks of confidential information outside the corporate network. In addition, modern information security systems are also capable of monitoring the company’s reputation and identifying unreliable employees.
Why is a confidential data protection system an indispensable element in building an effective security policy in an organization? Just check out the statistics provided by the think tank Gemalto for the 1st half of 2018:
18,5 million cases of data leakage per day;
771,9 data leakage cases per hour;
12,8 data leaks per minute;
214 data leaks every second.
But that's not all: compared to the first half of 2017, cases of confidential data leaks increased by 72%– from 938.8 million to 3.3 billion. Impressive numbers, right?
Therefore, the introduction of information security tools pursues the following goals:
Firstly, to protect intangible assets and intellectual property from misuse by third parties;
Secondly, to enlist the support of legal institutions - courts and law enforcement agencies, in case of violations of the rights of the legal owner by creating and providing an evidence base in case of incidents;
Thirdly, to ensure the possibility of applying sanctions to persons guilty of violating exclusive rights, as well as recovering damages from them.
So, you have decided that your business simply needs a DLP system and you intend to take this issue seriously. Where to begin?
Conduct internal research
Study the existing organizational and administrative documentation;
Agree on a list of signs by which potentially important information should be classified as confidential;
Evaluate the company’s information resources, distribute them into categories:
1) establish a list of positions and employees who need access to confidential information.
2) describe in detail the manipulations to which confidential information is subjected during business processes.
What is it for? Conducting an audit will allow you to identify the weakest points in existing business processes and get a complete picture of what still needs to be worked on, in order to ultimately get a solid foundation for deploying a DLP system in your organization.

Develop regulatory documentation
Based on the information received as part of the study, it is necessary to develop regulatory documentation. One of the basic requirements for the implementation of security policies is the introduction of a trade secret regime. To establish a regime, it is necessary to approve a document describing the list of restricted access information. Considering the fact that the DLP system is a mechanism for exercising the exclusive right to intellectual property and intangible assets, information classified as confidential must be determined in accordance with the law. Thus, according to Article 1225 of the Civil Code, protected intellectual property includes:
1) works of science, literature and art;
2) computer programs;
3) databases;
7) inventions;
8) utility models;
9) industrial designs;
10) selection achievements;
11) topology of integrated circuits;
12) production secrets (know-how)
15) names of places of origin of goods;
In addition, it is necessary to provide for the development of a document with a list of persons authorized to work with confidential information, and each employee responsible for compliance with the regime must be familiarized with this document against signature. A necessary requirement for legal support for the introduction of a trade secret regime is also the development of a document regulating the handling of confidential information within the organization and describing the mechanisms for its protection.
And finally, the last preparatory point is the issuance of an order to introduce a trade secret regime within the organization.
What is it for? Let us give a clear example from judicial practice:
On February 28, 2012, the Twelfth Arbitration Court of Appeal (Saratov) rejected the appeal of LuxuRita LLC against the decision of the Arbitration Court of the Saratov Region on the Company’s claim against individual entrepreneur Yu.Yu.V. about the recovery of 491,474.92 rubles. losses in the form of lost profits (illegal use of the client base and poaching of clients)
The court of first instance correctly established that the plaintiff did not take the measures established by Part 1 of Article 10 of the Federal Law “On Trade Secrets” in relation to the Company’s client base. The plaintiff did not provide evidence in the case materials confirming the introduction of a trade secret regime in relation to its client base.
If there are no grounds to recognize the plaintiff’s client base as a trade secret in relation to the provisions of Article 1465 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the defendant cannot be held civilly liable under the rules of Article 1472 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Talk to employees
Like any progressive technology, DLP systems have become significantly more advanced than their predecessors. Thus, modern DLP systems can combine several important functions at once and be not only a tool for protecting confidential data, but also, for example, an effective program for monitoring employee activities. This solution is optimal for managers interested in real analysis of staff performance, and will also allow them to quickly identify unreliable employees.
However, the introduction of monitoring in an organization requires the use of a number of measures, which include:
Development of monitoring regulations, which should detail the rules for the use, processing, storage and transfer of confidential information within the organization, as well as what liability is provided for their violation;
Familiarization of all company employees with the contents of the regulations against signature.
In addition, the regulations must contain a clause on how the information obtained during monitoring can be used in the future, and the stated information must correspond to reality. If it is necessary to conduct audio and video recordings as part of monitoring, notification of this must also be specified in the regulations.
Despite the widespread use of such systems in various areas of business, many are still concerned about the legality of implementing monitoring systems, because there is Article 23 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, which talks about privacy. However, this article is only valid in relation to personal life physical person and has nothing to do with the performance of official duties. Thus, when drawing up a document regulating the activities of an employee in an organization, it is necessary to indicate that:
all means of communication transferred to the employee for use are intended only to perform official duties;
the owner of the email and telephone network subscriber is organization Thus, they are provided to the employee for temporary use during the performance of official duties.
However, the employer also has certain obligations that he must comply with. For example, we will not allow the deliberate secret collection of personal information of employees for their own purposes.
Compliance with all the above requirements will allow you to effectively use the monitoring system without violating the rights of your employees.
What is it for? Control over work activities is by no means an innovation, but a prerequisite for establishing labor relations, prescribed in the labor code. And if we take into account the specifics of modern business, monitoring systems are a necessity. Let's give an example from life, where monitoring the activities of an employee allowed her to be caught in the illegal use of confidential information: “ On May 28, 2008, the Presnensky Court rejected the claim to replace the grounds for dismissal from Art. 81 clause 6 at Art. 77 clause 3 (at your own request).
An employee of the travel agency "Intercity Service" (KPM Group holding) K.B. Over the course of a year, she sent confidential information to another travel company both from her computer and from the computers of other employees.
The basis for dismissal for a one-time gross violation of labor duties by an employee - disclosure of a secret protected by law that became known to the employee in connection with the performance of his labor duties - was based on materials from an internal investigation involving the automation department.
As evidence, the court was presented with emails sent from a business email account to external mail addresses.
The reason for the internal investigation was an increase in outgoing traffic from an employee whose duties did not include conducting large-scale correspondence with non-corporate recipients.
Dismissed under Article 81 Part 6 of the Labor Code – disclosure of trade secrets.”

Comply with FSTEC requirements forDLP-systems
The Federal Service for Technical and Export Control (FSTEC), which is a national executive body authorized to ensure security in key elements of information infrastructure, has special requirements for DLP systems.
According to the recommendations of the methodological document “Measures for protecting information in state information systems”, approved by the FSTEC of Russia on February 11, 2014, the organizational and technical measures for protecting information taken are:
Must ensure the availability of information processed in an automated management system (exclusion of unlawful blocking of information), its integrity (exclusion of unlawful destruction, modification of information), and, if necessary, confidentiality (exclusion of unauthorized access, copying, provision or distribution of information);
Must be correlated with measures for industrial, physical, fire, environmental, radiation safety, and other measures to ensure the safety of the automated control system and the controlled (controlled) object and (or) process;
Should not have a negative impact on the normal operation of the automated control system.
In accordance with the recommendations for ensuring the integrity of the information system and information (OCI) presented in the document, the information system must control the content of information transmitted from the information system (container based on the properties of the access object, and content based on the search for prohibited transfer information using signatures, masks and other methods), and eliminating the unlawful transfer of information from the information system (OTSL. 5).
To meet the requirements, the functionality of a modern DLP system must include:
identifying facts of unlawful transfer of protected information from an information system through various types of network connections, including public communication networks, and responding to them;
identifying facts of illegal recording of protected information on unaccounted for removable computer storage media and responding to them;
identifying facts of unlawful printing of documents containing protected information and responding to them;
identifying facts of illegal copying of protected information into application software from the clipboard and responding to them;
control of storage of protected information on servers and automated workstations;
identifying facts of information storage on shared network resources (shared folders, document management systems, databases, mail archives and other resources).
Requirements made by FSTEC for strengthening information security measures for DLP systems:
the information system must store all information transmitted from the information system and (or) information with content that is unacceptable for transmission from the information system for a period of time determined by the operator;
the information system must block the transmission of information with unacceptable content from the information system.
What is it for?
Failure to comply with regulatory requirements entails a lot of troubles, so we strongly recommend that, firstly, you carefully study the regulatory documentation, on the basis of which the customer will develop an information security policy for your company, and secondly, contact only trusted companies offering a licensed software product , meeting all regulatory requirements, for example, SecureTower.
Don't stop there
A DLP system cannot be identified as a universal solution to all problems related to cybersecurity. Building a competent security policy in a company is, first of all, a process, not a task that requires constant improvement. Since the key characteristic of any process is its continuity, any changes within the organization - hiring and dismissal of employees, optimization of business processes, introduction of new documents, etc. - must also be recorded and reflected in the DLP system.
What is it for? When introducing a DLP system into a business, it is important to understand that it is just a tool that requires constant configuration, so only a responsible approach from management to using the system and timely changes to security policies can guarantee maximum protection against leaks.
In the modern world, one of the key economic resources is information. Whoever owns it will be successful, but at the same time, a data leak almost always means the loss of customers, or even the collapse of the company. This is why today there is so much interest in DLP solutions to identify and prevent the transfer of confidential information. The choice is large, the leaders have not yet been clearly defined, and proposals are often similar in function, but differ in the logic of work and the underlying principles, so it is not so easy to decide.
How to choose DLP?
Information security has become one of the components of the activities of any company, and the corresponding risks affect its rating and attractiveness to investors. According to statistics, the likelihood of a leak of confidential information due to the actions of an organization employee (insider) exceeds the likelihood of a leak as a result of hacking, and these are not necessarily intentional actions; the user can accidentally send a file to the wrong recipient. Before the advent of the Internet, it was almost impossible to control the activities of employees. No, it was, of course, possible to establish control, but there were no technical means to automate the process. Now everything has changed. Business correspondence is carried out via e-mail, users communicate via IM and VoIP, exchange files, write blogs, publish messages on social networks, etc. All these channels are easy to control automatically, the power of modern servers and storage capacity allow you to collect and process data in real time . To detect and prevent the transfer of confidential data at different stages (during movement, use and storage), a whole class of protection systems is used - DLP (Data Leak Prevention). Today there are a dozen more synonymous terms for such systems: ILDP (Information Leak Detection & Prevention), IPC (Information Protection and Control), ILP (Information Leak Prevention), etc. Their task is, in general, simple - monitoring, identification and protection. There are no official standards yet that define what DLP should be, so developers have different views on DLP features. You can often find a variety of implementations, which do not always include what is really necessary or, on the contrary, are crammed with unnecessary functionality added by order of the company. However, over time, some requirements have emerged that a full-featured DLP solution must have. First of all, they relate to the range of possible leakage channels:
- email (SMTP, POP3, IMAP);
- IM/VoIP messaging programs and P2P clients;
- web resources (social networks, forums, blogs), as well as file transfer via HTTP, HTTPS and FTP protocols;
- network printing (SMB Printing, NCP Printing, LPD, etc.);
- external devices (USB, CD/DVD, printers, Bluetooth, modems, etc.), network folders.
The nature of the transmitted data is determined by detecting specific features (tags, hash functions, vultures) and analyzing the content (statistical analysis, regular expressions, etc.). Good systems, as a rule, use all available technologies, and the administrator can easily create rules independently based on prepared templates. In addition, the DLP system must provide the security service with a tool for analyzing all events and an archive of transmitted information. Another criterion that determines the choice of DLP is the ability to block data leakage in real time. However, experts have different views on this function, because an error in the operation of DLP (and false positives do occur, especially at the commissioning stage) can lead to the blocking of completely legal traffic, and therefore interfere with the work of employees. Therefore, many administrators prefer analysis after the fact rather than blocking.
INFO
An important stage in the deployment of DLP is implementation, when it is necessary to clearly articulate requirements and expectations and “provide” the DLP with all the data for control.
Websense Data Security Suite
- Project website: websense.com.
- License: proprietary.
- Server OS: Windows Server 2003 R2.
- OS clients: Windows Vista, 7, 2003, 2008/R2.
- Russification: absent.
The California-based Websense corporation is well known as a manufacturer of web traffic filtering systems; in particular, Facebook will soon implement its development for protection when clicking on external links. The solutions are aimed primarily at medium and large companies with over 500 employees and government agencies. The Websense DSS complex, by monitoring the main data exchange channels, allows you to stop the leakage of confidential information in real time. It is powered by PreciseID fingerprinting technology developed by PortAuthority Technologies, which Websense acquired in 2006. PreciseID provides high accuracy in detecting sensitive data and does not have some of the disadvantages of linguistic methods. Data is described using a “digital fingerprint,” which is a set of characters or words in a document or the contents of database fields. This approach provides accurate content classification for more than 400 document formats (including DBMS tables and compressed files), even if the data is migrated or converted to another format. In addition to PreciseID, other algorithms are used: dictionaries, exact and partial matches, statistical analysis, etc. However, to analyze information, Websense products use several technologies “Deep Content Control” and ThreatSeeker (scanning websites and detecting new threats) .
The main transmission channels are monitored: email (SMTP), MS Exchange messages, HTTP/HTTPS, FTP, IM/MSN. ICAP integration is provided with any Internet gateway that supports this protocol. For monitoring, the Websense server can be installed in a gap or use traffic mirroring (SPAN).

Websense DSS automatically determines the response to an incident or requires confirmation from the responsible employee. The system can block the transfer of confidential data, send a notification (to a security specialist, boss or content owner), launch an external program, send a request for confirmation of sending, etc. The system assigns a unique number to the incident and attaches a file to the message. The administrator sets flexible policies taking into account the company's business processes, and the package already includes several dozen templates and customized reports on incidents and user activity. Websense products allow you to restrict access to certain information for individual employees or groups, and protect corporate documentation from unauthorized changes. Other features include forced email encryption (via a gateway) and collaboration with other Websense products (such as the Websense Web Security Gateway). Integration with Active Directory, Novell eDirectory and Lotus Domino is supported. A number of other applications are used in conjunction with Websense DSS, expanding the capabilities of the DLP complex:
- Data Endpoint - installed on end PCs, where it controls data transferred via USB and when printing, attempts to take screenshots, IM messages, etc.;
- Data Monitor - monitors transmission channels to determine who sends what, where, how and what, and compares it with policies and business processes, reducing risks;
- Data Protect - includes Data Monitor, automatically blocks data leaks based on policies;
- Data Discover is a program for searching and classifying confidential data, which can be used either as part of DSS or separately; it does not require installing agents.
All Websense solutions are managed using a single Websense TRITON Console (Java and Apache Tomcat). Websense DSS is very easy to install. The archive already includes MS SQL Server Express 2008 R2, but for large environments it is better to use the full version. The initial setup of policies is done using a simple wizard that creates templates taking into account the country and nature of the organization’s activities, including regional settings for Russia.
Falcongaze SecureTower
- Project website: falcongaze.ru.
- License: proprietary.
- Server OS: Windows 2003/2008 (x86/x64).
- OS clients: Windows XP/Vista/7/2003/2008 (x86/x64).
- Russification: yes.
A relatively young solution developed by the Russian OOO Falcongaze. It is a software product that uses content, attribute and statistical analysis technologies (keywords, regular expressions, fingerprint, etc.) to search for confidential information. Provides control over all popular data leakage channels, including monitoring encrypted traffic (HTTP/S, FTP/S, POP3/S, SMTP/S, IMAP, OSCAR, MMP, MSN, XMPP). If the organization uses MS Exchange 2007/2010, then all internal and external correspondence is also checked for compliance with policies. I would especially like to highlight the full support of Skype, because SecureTower can intercept voice traffic, text messages, files and sent SMS. Not all DLPs can do this or provide it in full (usually the installed agent only controls text messages). Traffic interception can be configured selectively: by IP addresses or ranges, MAC addresses, ports and protocols, logins, file sizes, etc. The system recognizes password-protected MS Word/Excel, PDF documents and some types of archives. When a user submits a password-protected document or archive, it generates an event and provides the administrator with complete information and a copy of the file. SecureTower controls data copied to external devices, printing to local and network printers. To avoid errors when determining the sender, SecureTower, in addition to the generally accepted information received from the domain, analyzes all contact information, IP address and period of its use, login in various messengers, etc. Next, the system creates personal cards, with the help of which all collected information is linked to accounts (integration with Active Directory is possible).

In addition, SecureTower has features that are not specific to DLP, but are highly sought after by most organizations. Thus, with its help you can monitor the work of employees - the system periodically takes screenshots for subsequent viewing in chronological order, and tracks internal and external contacts. At the same time, visual interactive reports are generated that allow you to dynamically monitor network events and the activity of individual users. Based on the collected data, it is very easy to find out how much time the employee spent on empty communication, neglecting his job duties, and when this happened. Functionally, SecureTower consists of several components:
- traffic interception server - captures network traffic and transfers it to the database for storage (the most resource-demanding component);
- workstation control server - used to deploy agents to workstations, monitor their work and collect information intercepted by agents (including encrypted traffic and data on work with external devices);
- information processing server - processes, indexes and analyzes data, searches, sends notifications, generates reports, etc.
MS SQL Server, Oracle, SQLite and PostgreSQL can be used as a DBMS. The system is easily scalable; if necessary, a new server can be added to the network, responsible for intercepting or processing data. The deployment process is very simple, using the Falcongaze SecureTower Admin Console and the Falcongaze SecureTower Client security console for management, rule creation and analysis. In the installed system, several general rules are active that allow you to identify the sending of a number of data (credit card numbers, TIN), visiting social networks, sending a resume to look for a new job, etc.
OpenDLP capabilities

An Enterprise version is offered for a fee, which has advanced analysis tools, an improved interface, quarantine, an archiving function and provided support.
Conclusion
It must be remembered that DLP is, first of all, a tool that allows you to significantly reduce risks, the presence of which in itself disciplines employees. It is also not worth expecting that the implementation of such a system will guarantee protection against leaks resulting from deliberate actions. If an insider wants to transfer or remove valuable information, he will certainly find a way to do this, so all traditional methods of protection should also be used.
Even a novice system administrator can handle installing a DLP system. But fine-tuning DLP requires some skills and experience.
The foundation for stable operation of DLP class products is laid at the implementation stage, which includes:
- identification of critical information that must be protected;
- development of a privacy policy;
- setting up business processes to address information security issues.
Performing such tasks requires narrow specialization and in-depth study of the DLP system.
Classification of protection systems
The choice of a DLP system depends on the tasks that a particular company needs to solve. In the most general form, tasks are divided into several groups, including monitoring the movement of confidential information, monitoring the activity of employees during the day, network monitoring (gateway analysis) and complex monitoring (networks and end workstations).
For the purposes of most companies, choosing a comprehensive DLP solution will be optimal. Hosted systems are suitable for small and medium-sized businesses. The advantages of hosted DLP are satisfactory functionality and low cost. Among the disadvantages are low performance, scalability, and failure tolerance.
Network DLP does not have such disadvantages. They easily integrate and interact with solutions from other vendors. This is an important aspect, since the DLP system must work seamlessly in tandem with the products already installed on the corporate network. Equally important is the compatibility of DLP with the databases and software used.
When choosing DLP, the data transmission channels that are used in the company and need protection are taken into account. Most often these are email, IP telephony, and HTTP protocols; wireless networks, Bluetooth, removable media, printing on printers, networked or working offline.
Monitoring and analysis functions are important components of the correct operation of the DLP system. Minimum requirements for analytical tools include morphological and linguistic analysis, the ability to correlate monitored data with dictionaries or saved “standard” files.
From a technical point of view, modern DLP solutions are largely the same. The effectiveness of the system depends on the proper configuration of the automation of search algorithms. Therefore, the advantage of the product will be a simple and understandable process for setting up DLP, which will not require regular consultations with the vendor’s technical specialists.
Implementation and configuration approaches
Installation of a DLP system in a company most often follows one of two scenarios.
Classic approach means that the customer company independently establishes a list of information that needs protection, the features of its processing and transmission, and the system controls the information flow.
Analytical approach lies in the fact that the system first analyzes information flows in order to isolate information that needs protection, and then fine-tuning occurs to more accurately monitor and ensure the protection of information flows.
|
STAGES OF DLP IMPLEMENTATION |
|
|
according to the classical scheme: |
according to the analytical scheme: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Problems during DLP operation
Practice shows that most often the problems with the functioning of DLP systems lie not in the technical features of the work, but in the inflated expectations of users. Therefore, an analytical approach to implementing security works much better; it is also called a consulting approach. Companies that are “mature” in information security issues, who have already encountered the implementation of tools for protecting confidential information and know what and how best to protect, increase their chances of building a well-functioning, effective protection system based on DLP.
Common mistakes when setting up DLP
- Implementing template rules
Often, the information security department is assigned the role of a service department for other divisions of the company, which provides “clients” with services to prevent information leaks. While for effective work, information security specialists require a thorough knowledge of the company’s operational activities in order to “tailor” the DLP system taking into account individual business processes.
- Not covering all possible channels of confidential data leakage
Control of email and HTTP protocols using a DLP system with uncontrolled use of FTP or USB ports is unlikely to provide reliable protection of confidential data. In such a situation, it is possible to identify employees sending corporate documents to personal email in order to work from home, or slackers spending working hours on dating sites or social networks. But such a mechanism is useless against deliberate “leaking” of data.
- False incidents that the information security administrator does not have time to process manually
Saving the default settings in practice results in an avalanche of false alerts. For example, upon requesting “bank details,” an information security specialist is bombarded with information about all transactions in the company, including payments for office supplies and water delivery. The system cannot adequately process a large number of false alarms, so some rules have to be disabled, which weakens protection and increases the risk of missing an incident.
- Failure to prevent data leakage
Standard DLP settings allow you to identify employees who are engaged in personal matters at work. In order for the system to compare events on the corporate network and indicate suspicious activity, fine tuning will be required.
- Deterioration in DLP efficiency due to the alignment of information flows around the system
The information security system should be “customized” on top of business processes and accepted regulations for working with confidential information, and not vice versa - adjusting the company’s work to the capabilities of DLP.
How to solve problems?
In order for the protection system to work like clockwork, you need to go through each and every stage of DLP implementation and configuration, namely: planning, implementation, verification and adjustment.
Planning
It consists of a precise definition of the data protection program. The answer to a seemingly simple question: “What will we protect?” - not every customer has it. A checklist made up of answers to more detailed questions will help you develop a plan:
→ Who will use the DLP system?
→ Who will administer the data?
→ What are the prospects for using the program within three years?
→ What goals does management pursue when implementing a DLP system?
→ What are the reasons for the atypical requirements for preventing data leaks in a company?
An important part of planning is to clarify the object of protection, or in other words, to specify the information assets that are transferred by specific employees. Specification includes categorization and recording of corporate data. The task is usually separated into a separate data protection project.
The next step is to determine the real channels of information leakage; this is usually part of an information security audit in a company. If detected potentially dangerous channels are not “closed” by the DLP complex, you should take additional technical protection measures or choose a DLP solution with more complete coverage. It is important to understand that DLP is an effective way to prevent leakage with proven effectiveness, but cannot replace all modern data protection tools.
Implementation
Debugging the program in accordance with the individual requests of a particular enterprise is based on the control of confidential information:
- in accordance with the characteristics of special documentation adopted by the company;
- in accordance with the characteristics of standard documentation common to all organizations in the industry;
- using rules aimed at identifying incidents (atypical actions of employees).
Three-stage control helps identify deliberate theft and unauthorized transfer of information.
Examination
The DLP complex is part of the enterprise information security system, and does not replace it. And the efficiency of a DLP solution is directly related to the correct operation of each element. Therefore, before changing the “factory” configuration to suit individual needs, companies conduct detailed monitoring and analysis. At this stage, it is convenient to calculate the human resources required to ensure stable operation of the DLP program.
Adjustment
After analyzing the information collected during the test operation stage of the DLP solution, we begin to reconfigure the resource. This step includes clarifying existing and establishing new rules; changing tactics for ensuring the security of information processes; staffing to work with the DLP system, technical improvement of the program (often with the participation of the developer).
Modern DLP systems solve a large number of problems. However, the full potential of DLP is realized only through an iterative process, where analysis of system performance results is followed by refinement of DLP settings.
10/08/2018, Mon, 10:49, Moscow time
A full-fledged hybrid DLP system allows you to provide reliable protection against data leaks and monitoring of network traffic on the widest range of data transmission channels. At the heart of these capabilities is the effective use of the strengths of network-centric and endpoint DLP architectures in various scenarios and in different formulations of the problem of preventing and controlling data leaks.
In most DLP systems on the Russian market, the defining element is a network traffic interception server, usually operating in passive mode. In such systems, an endpoint agent is almost always present to solve tasks that are incompatible with traffic control at the gateway level - control of devices and some web services and protocols. However, the presence of an agent is not yet a sign of a full-fledged hybrid DLP; it is just a distribution of different control functions across different components.
The key task of the DLP server component, which works with a copy of the organization’s network traffic as a whole, is to control the use of network data transmission channels by employees when the user is inside the corporate perimeter, including collecting evidence and detecting information security incidents. At the same time, the endpoint agents of the hybrid DLP solution are designed to solve the problem of monitoring the use of removable drives, the print channel, and network applications with proprietary encryption. In these tasks, real-time content filtering is used for all potential data leakage channels in DLP systems that claim to be full-featured agents.
The first such example of hybrid DLP on the Russian market is the updated version of DeviceLock DLP 8.3, supplemented by the DeviceLock EtherSensor server module. A hybrid DLP system effectively solves several problems and challenges facing information security services. This is monitoring network traffic from computers and mobile devices on which, for technical reasons, it is impossible to install or operate a DLP agent, or reducing the load on user workstations through separate control of various network services and protocols at different levels. Automatic switching of different combinations of DLP policies to control network traffic in the DeviceLock DLP agent depending on the presence of a connection to the corporate network and/or corporate servers allows for extremely flexible user control. For example, at the agent level, when a laptop is in the office, control of devices, printers and particularly critical network applications and services is maintained, including the use of real-time content filtering, while control and inspection of other network protocols and services is assigned to the EtherSensor module. A unified database of event logging and shadow copying, filled with events and data obtained by intercepting traffic from the network level and as a result of monitoring network communications and devices on workstations, allows you to identify information security incidents for a wide range of potential data leakage channels.
Typical scenarios
Let's look at several typical scenarios for using DeviceLock DLP as a hybrid DLP system. A very common scenario when full control of network traffic with blocking of data transfer is impossible or inapplicable. This situation arises when using guest computers and mobile devices in a corporate network, as well as for workstations running Linux and MacOS. In addition, intercepting and analyzing network communications directly on workstations may be impossible or excessively resource-intensive on workstations with weak computing power. The solution to the problem of monitoring network traffic in such a scenario is provided by intercepting and analyzing traffic at the network level - listening to traffic from mirror ports of the server, integration with NGFW devices and proxy servers, and other methods that do not require installing an agent on workstations, which is successfully provided by the server EtherSensor. In this case, the task of DLP control of peripheral devices and workstation ports is performed by the DeviceLock agent (on Windows and MacOS operating systems), and the DeviceLock Enterprise Server database collects events and data from both EtherSensor in terms of network traffic objects and from DeviceLock agents regarding device control.
A unified database of event logging and shadow copying, filled with events and data obtained by intercepting traffic from the network level and as a result of monitoring network communications and devices on workstations, allows you to identify information security incidents for a wide range of potential data leakage channels
The second typical scenario is monitoring network communications when blocking data transmission over the network is unacceptable. In some organizations, the task of monitoring network traffic is limited to logging and analyzing the archive of intercepted data due to a number of factors. For example, to implement full-fledged DLP control with blocking leakage of limited access data, there are not enough resources of the information security service, or passive control is determined by the company’s management as sufficient due to the already introduced restrictions on the use of network communications in general at the network perimeter level, or management is afraid of the risk of interference in the built business -processes with network information exchange. There are cases when an organization does not assess the risks of data leakage as critical for the business, or, finally, there is no way to classify confidential data or determine criteria for detecting restricted data to apply content filtering mechanisms and prevent leakage of such data.
In this scenario for using DeviceLock DLP, the organization receives at its disposal a traditional Enterprise-level DLP system capable of monitoring and analyzing traffic on very large flows (up to analyzing traffic from hundreds of thousands of employees) with low deployment and ongoing operating costs, as well as negligible requirements for technical equipment. The solution in this scenario is fully consistent with the previous scenario, but with the difference that when the need arises to block unacceptable attempts to transmit restricted data, or there is an understanding of the criteria for identifying confidential data and the ability to use content filtering. In this case, this scenario flows into another variation - the use of a full-fledged hybrid DLP system for individual employees, departments or throughout the entire organization.
Complex scenarios
Further development of the logic of combining the capabilities of DeviceLock agents and the EtherSensor server leads us to scenarios that are more complex to implement, but at the same time much more effective in preventing leaks of confidential data.
First of all, this is a scenario that provides for separate control of network communications, when depending on the current status of the connection to the corporate network (availability of a local network connection, availability of a domain controller, availability of a DLP server), the degree of relevance of access to corporate information may vary. To solve such problems, a flexible approach to implementing information protection from leaks is required. Automatic switching of various combinations of DLP policies for monitoring network traffic (various combinations of rules and control parameters) in the DeviceLock DLP agent, depending on the presence of a connection to the corporate network and/or corporate servers, allows for extremely flexible, separate control of user network communications. For example, at the agent level, when the laptop is in the office, control of particularly critical network applications and services is maintained, including the use of real-time content filtering to prevent leakage of confidential information, and inspection of other network protocols and services is assigned to the EtherSensor module. When the DeviceLock agent on a protected workstation is switched to offline mode, policies are automatically switched to the maximum required level of network communications control, taking into account the possible inaccessibility of outgoing network traffic from the workstation to the EtherSensor server.
As a result of separate control using automatic switching of online and offline modes in the DeviceLock agent with traffic monitoring at the EtherSensor server level, full control of network communications is achieved, regardless of the location and method of connecting controlled computers to the Internet. This approach will be especially productive for monitoring mobile employees who use laptops and laptops to work outside the office.
The scenario of selective control of network communications will be even more effective. Thanks to the combined use of endpoint agent functionality and server-based network traffic interception technologies, the full capabilities of the hybrid system are achieved. This is the most powerful network communications control scenario available today.
In such a scenario, the most critical part of network applications considered as potential channels for leaking confidential data (for example, instant messengers with the ability to transfer files), as well as local ports and devices, are controlled by the DeviceLock agent. In real time, the agent analyzes the contents of restricted data transfer processes (also at the agent level, “in the gap”). Based on the results, a decision is made on the admissibility of the transfer, or on the creation of a shadow copy for incidents that are significant for the purposes of investigation, or on sending an alarm when the DLP rule is triggered. Control of other network communications considered to have a lower degree of risk from the point of view of combating data leakage (when monitoring and analysis of transmitted data is sufficient to solve information security problems, for example, for surfing websites and job search services) is performed by the EtherSensor server through interception and analysis network traffic at the perimeter level. Briefly speaking, this network traffic control model can be described as “Monitoring all traffic (EtherSensor) + Selective blocking of invalid attempts (DeviceLock DLP agent).” What is important is that policies for enabling or unblocking any network protocols and services, both at the context level and in content-dependent rules, can be changed and applied by the information security service at any time without rebooting user workstations and without user intervention.
In this scenario, a qualitative balance of opportunities and risks is achieved: the risks associated with blocking are delegated to agents on protected computers, while the tasks of monitoring network traffic and detecting security events throughout the network as a whole are entrusted to the EtherSensor server.
If we go further, it can be considered - and quite easy to implement! – the most powerful scenario for using a modern hybrid DLP system, when in addition to the ability to separate control levels (monitoring and blocking data transfer) between the agent and the DeviceLock DLP DLP system server, a selective approach is added for different users and user groups, or for different computers and groups computers.
In this option, full-featured DeviceLock agents perform directly and only on protected workstations all DLP functions (access control, logging, alarm notifications) and only for specified users and user groups. The network activity of users and groups that require free access to various network communication channels to perform business tasks is monitored by the EtherSensor server by intercepting and analyzing network traffic at the perimeter level.
This scenario is also extremely productive for controlling so-called risk groups, when special sets of policies are created on DeviceLock agents for DLP control of various accounts, and switching of applied policies is performed in real time by including such users in a group of users corresponding to a particular group risk.
In any scenario of simultaneous use of the DeviceLock EtherSensor server module in combination with Endpoint components of the DeviceLock DLP complex in hybrid DLP system mode, a unique opportunity opens up to create flexible DLP policies with different levels of control and response to events. The simultaneous use of two different DLP architectures (network and agent) to control network traffic significantly increases the reliability of solving the problem of preventing and identifying information leaks. Vakhonin Sergey. Director of Solutions at DeviceLock, Inc.
Sergey Vakhonin, Director of Solutions at DeviceLock, Inc.
Good afternoon
The most popular way of exchanging corporate information today remains email. It is there that employees send scanned copies of documents, projects for approval, invite them to meetings, inform about events, etc. Sometimes email correspondence is equated to official correspondence between organizations at the level of letters from first persons. Therefore, this information transmission channel is an object close attention from representatives of information security departments/services(they monitor the leakage of confidential information) and the economic security block (they monitor correspondence, look for kickbacks, collusion, searches for a new job, forgery of documents, etc.)
A little about the theory. You've probably noticed that your mail does not immediately reach your counterparties and/or the evil guys from the ugliness service are interested in one or another of your shipments after some time, especially if you send any personal data without using the security measures taken. These circumstances indicate that your organization has some kind of so-called DLP system installed. Without going into technical details, I will give information from the wiki:
Leak prevention system(eng. Data Leak Prevention, DLP) - technologies for preventing leaks of confidential information from an information system to the outside, as well as technical devices (software or firmware) for such leak prevention. DLP systems are built on the analysis of data flows crossing the perimeter of the protected information system . When confidential information is detected in this flow, the active component of the system is triggered, and the transmission of the message (packet, flow, session) is blocked or passes but leaves a mark.
In general, roughly speaking, this is a means of monitoring the actions of employees and its main goal is to “find what is prohibited.” We will discuss whether this is legal in the next article. And the principle of the system’s operation can be compared to a filter, that is, you sent a letter, and if it was included in the filter according to the criteria and, depending on the system settings, it was blocked or passed on to the recipient, but at the same time notifying fellow security guards.
Let's see how you can determine whether one of these systems is installed in your organization. In order to find out whether such a tracking system is installed in your organization, first of all, you can look at the concluded agreements for the purchase or maintenance of such systems. We are looking among them most popular developer companies:
Jet Information Systems
and less popular:
McAfee, Falcongaze, GTB, "Trafika", Iteranet, RSA, Trend Micro, Verdasys, Stakhanovets.
If you don’t have access to contracts, you can monitor the government procurement website (if your office is the government’s). As you can see from the image below, the subject of the agreement can be different - from the acquisition of non-exclusive rights to technical support, the main thing in the search is to enter the name of the development companies from the list that I provided.

If these methods do not help, then you can understand that you are being followed by checking with the recipient by phone to see how long it takes for them to receive letters (only if the letter is blocked before sending), or you can ask your IT specialist friends if they have a mail message monitoring system installed In the organisation. You can, of course, try to find running processes on your computer, because... tracking system agents (system components) are installed personally on all employees’ workstations, but the fact is that these processes are skillfully hidden under standard MS Windows processes and without the proper level of knowledge it will be quite difficult to determine the process launched by the agent.
Now let's look at how we can bypass this system. Remember that the implementation of the techniques from the article depends on the specific DLP settings and can only be implemented through trial and error. So do it at your own risk.
Most importantly, do not try to bypass the systems by trying to make the document font white or trying to hide sheets and deadlines in MS Exel documents, all this will be immediately seen by fellow security officers!
So our task is convey information in the form of files or text via email, knowing that the organization has a DLP system deployed and functioning. Of course, many of you will say why such difficulties - “I can take a photo of the contents of the screen with my phone and that’s the end of it,” but in some places it is forbidden to use phones, and in some places colleagues will look at it unkindly (especially in open-space offices) ), and sometimes they will tell you where to go, sometimes it is a document in an editable format that is needed, and not a photo of it on a mobile phone; in general, there are many options. So let's give examples of transmitting such information:
1. Dispatch after business hours.
The simplest and most banal thing that can happen is to simply send your letter to the desired email address after the end of the working day. This method is successful if the system is configured to intercept email messages, for example, from 9-00 to 18-00 on weekdays and block them at the specified time. This is due to the fact that fellow security guards who can, if anything happens, unblock a stuck letter just like you, work under an employment contract the same hours as you, so after the end of the working day they turn off the system or it stops automatically. You can check whether this setting is relevant by sending a couple of harmless messages after 18-00 and see if messages that, for example, did not arrive immediately during the working day, will be received immediately. I'll tell you right away not the best option, because Regardless of the result of sending, a trace of what you sent will remain in the system, and if the system is properly monitored by security guards, they will see your sending.
2. Removing beacon words
This method involves setting up DLP to search by keywords, i.e. it looks for dictionary matches in the sent document. In the case of monitoring rollbacks, such a dictionary may contain the following group of words: grandmothers, greens, cabbage, etc. In case of preventing leaks of confidential information, this dictionary may contain the following vocabulary set: trade secret, company secret, confidential, chipboard, personal data, snils, power of attorney, passport, series number, etc. The method consists in removing such words that will clearly be present in a confidential document and identify it as classified information. Review the document you need to send for the presence of such words and delete. The method is also not the best because... No one will ever tell you the specific set of words contained in the dictionary.
3. Archive with password.
This method consists of encrypting a document in a standard *.rar archive and sending it to email. I would like to note right away that an archive with a password immediately arouses suspicion and in many systems is blocked and even decrypted. To protect yourself as much as possible you need to:
a) When setting a password for the archive, check the “encrypt file names” box. This is necessary so that the file names in the archive are not visible until the archive is opened with a password.
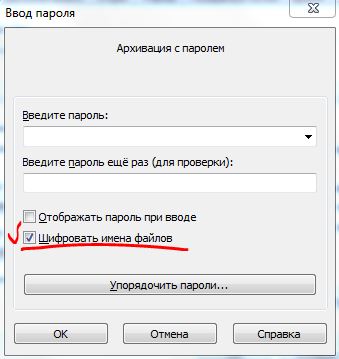
b) When choosing a password, you should pay attention to its length and complexity. Yes, this is necessary to prevent dictionary search if one is used in the system. Use a minimum of 10 characters containing lowercase and uppercase letters, special characters, spaces, and numbers. For example, our password will be $Op123KLM!987@. Don’t rush to type it into the input field, see part “c”.
V) The most important thing is to enter the password correctly in the input field in the archiver, now I’ll explain why. The fact is that agents installed on employees’ workstations can contain keylogger functionality and record all your actions (keystrokes) on the keyboard. It is worth noting that the key input record is tied to a specific process where typing is carried out (word, exel, winrar, etc.). To confuse your tracks, you can do the following (for example, we will use our password $Op123KLM!987@): For example, like this: open notepad and enter the first 4 characters from the middle of the password “KLM!” and after that we copy and paste into winrar, then in MS Word we enter the first 5 characters of the password “$Op123”, copy and paste into the beginning of the winrar input field, the last 4 “987@”, so as not to leave any traces of the input at all, we enter into virtual keyboard online keyboard using the mouse, and copy it to the end of the password entry field and click “ok”, write the password on a piece of paper, send the archive in a letter and inform the receiving party by phone, and eat the piece of paper:

There are plenty of such virtual keyboards on the Internet. It is worth noting that you can experiment as you like - type the wrong password, erase, move characters, but the tracking system will display a complete mess. It is better not to check the box for display password when entering - since the system may have a module for photographing your monitor installed .
3. We code online
The easiest way to transfer a document is to use online file sharing services; for example, we will look at www.rgho.st
We upload our file “Counterparty Database.docx” there and get a link:

Now we need to encrypt the link and send it via email. For an encryption example, we use the online service http://crypt-online.ru/crypts/aes/ with a symmetric AES antigorite. Insert the address of our link into the text field and select the encryption key size of 128-256 bits. Enter the password, in this case “site”, click encode and get the encrypted text:

We copy the result and send it in an email, providing the password and key length via an alternative communication channel (telephone). The recipient does the reverse conversion, enters the ciphertext and password and receives a link:

4. Steganography online
In order to avoid sending suspicious ciphertext, we can also use online steganography. Think about what documents you most often send to counterparties (reconciliation statements, invoices, etc.) and insert the code into the body of these files. For example, we will use a company card and the online service http://stylesuxx.github.io/steganography/. An enterprise card in the format of a regular picture, where the details of the organization are indicated. Load the card (file karto4ka.png), insert the text that we want to encrypt (our same link) and click “Encode”


The recipient does the opposite. Loads the file “karto4ka2.png” and clicks “Decode” and receives the desired link.

In addition, you can use portable steganography utilities, we will consider them in the following articles
Note: Information for research, training or audit purposes. Use for personal gain is punishable by Russian legislation.
